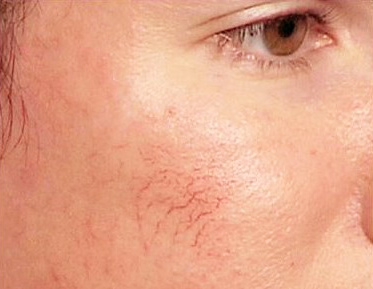
Cystic Acne
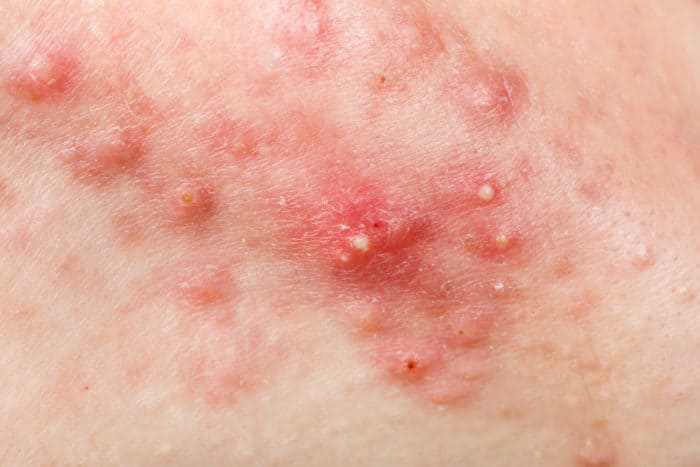
 Cystic Acne, also referred to as nodulocystic acne or inflammatory acne, is the grand stage for acne and most radical form. Severe inflammation accompanied by large, painful blemishes, is not uncommon to this form of acne. Cystic acne can occur on all areas of the body, typically the upper back and chest, but is most recognized to affect the face.
Cystic Acne, also referred to as nodulocystic acne or inflammatory acne, is the grand stage for acne and most radical form. Severe inflammation accompanied by large, painful blemishes, is not uncommon to this form of acne. Cystic acne can occur on all areas of the body, typically the upper back and chest, but is most recognized to affect the face.
Consisting chiefly of cysts and nodules, these spongy, pus-filled protrusions engraved beneath the dermal layer are considered to be worst and most severe degree of acne.
- A Nodule is a solid, aggregation of cells that form deep under the surface of the skin which are very painful and require weeks to heal.
- Cysts or “boils” are larger forms of nodules occur from accumulated sweat in hair follicles and affects deeper skin tissue than other more common forms of acne.
The lesions are caused by androgen stimulation associated with skin structures that contain hair follicles. The aggression of hormones causes sebaceous (oil) sub-units to over-stimulate oil which results in blockage at the follicle.
Some acne experts suggest that cysts are nothing more than inflamed nodular activity while someone without cystic lesions would be more aptly categorized as having “nodular acne”. Regardless of the classification, acne of this form should always be treated under the strict supervision of licensed professional.
Who is affected
Cystic acne affects mainly adolescents due to a massive increase in testosterone accompanied by puberty, though can occur into adulthood and in both genders. There is no hard evidence that acne is hereditary, though some experts will say that you are more than likely to experience acne if your parents did as well.
Causes
The main factors that cause cystic acne are:
- Over-stimulation of sebaceous glands,
- Surplus of dead skin cells clogging pores,
- Abundance of Propionibacteria acne (P. acne) present.
Blood toxins mix with P. acne bacteria that feed on oil, causing a rupture in the follicles wall. The body responds to the trauma with white and red blood cells to the damaged area. This is called inflamed acne.
Blood cells engorge the affected area to encapsulate the bacterium for degradation (to eat the bad bacteria and destroy it), though they leak into the dermal layers. If leak is shallow, or near the skins surface, it will heal quickly. A deeper break causes the blood cells to enter into adjoining follicles, forming nodules. When a membrane forms around the infection within the dermis, a cyst is formed.
Contrary to some opinions, cystic acne is not the result of poor hygeine or diet even, though these things don’t help, it occurs as the result of a hormonal imbalance and is no fault of the acne sufferer.
Cystic Acne effects and scarring
The effects of cystic acne are severe and lasting, causing irreversible scarring due to tissue damage from the inflammation. Scars are the body’s attempt at healing itself, yielding an over-abundance of collagen in one particular place. Attempts at picking or popping will most certainly scar your skin and pro-long your acne break-out.
Typically, acne carries with it the burden of shame and embarrassment for those who bear it. Some acne sufferers develop unhealthy avoidance avoidance behavior to social situations due to their skin maladies. Acne damages confidence, esteem, and can even lead to mild states of depression. Fortunately, for most, acne subsides in early adult-hood.
Cystic Acne treatment
Oral Retinoids (antiboitics)
Vitamin A derivative Isotretinoin (i.e., Accutane, Sotret) administered over a 4 – 6 months period. Effective in reducing sebum (oil) secretion from glands. Requires close medical supervision due to side effects, some of which can be severe.
Isotretinoin has proven very effective in the past and shown to clear up 80% of patients completely. Though, may cause depression and birth defects in pregnant women.
Dermabrasion
Cosmetic procedure usually involving the removal of the surface layer of skin through abrasion or sanding to reduce the appearance of scarring from acne or sun-damage. Can be very painful leaving the skin raw and requires local anesthesia. It takes several months for the skin to re-grow and heal. This type of dermabrasion is useful when the scar is raised, though less effective with sunken scars. CO₂ laser dermabrasion has become very popular due to the fact that it is blood-less, easier to gauge and control when compared to classic dermabrasion.
Blue & Red Light Therapy
Visible light at 405-420 nm twice a week has proven very effective at treating acne. Short wavelengths of light generate free radicals which act to kill P.acne bacteria in the absence of UV light so it is safe on the skin. Development of bacterial resistance is unlikely. When used regularly after three months patients saw a 76 to 80 % reduction in overall lesions. These units can be found at local tanning bed operations and are approved by the FDA.
Laser Treatment
Used to reduce acne scarring in one of three ways
- Burn away the hair follicle itself
- Burn away the oil gland
- Kill bacteria by depriving oxygen. It is however very expensive.
Surgery
Boils can be lanced and drained through surgical procedures if necessary.
Alternative Medicines
- Tea Tree Oil (melaleuca oil) – It has anti-inflammatory properties used in skin infections. Comparable to benzoyl peroxide without the same drying effect; kills P. acnes.
- Egg Oil – It has anti-bacterial and anti-inflammatory properties for skin infections due to the number of anti-oxidants it contains.
Vitamin B5 (Pantothenic Acid)
As we have mentioned, cystic acne is primarily caused by excessive oil secretion due to a hormonal imbalance or over-stimulation of androgens (steroid hormones). Pantothenic acid works by handicapping the sebaceous glands and preventing them from being able to secret oil to the skin’s surface much like that of Accutane, without the severity of the side-effects. It does this through the simple manipulation of key enzymes utilizing co-factors that are already abundant in our bodies.
Parents of teens who are starting the use of such prescription drugs should make sure that they are fully informed of the dosage levels and treatment schedule to keep them on track. They should also implement an immediate change in diet and hygiene practices to give them additional assistance to battle the acne infections. With that kind of commitment and the aid of good medical advice, full recovery can be expected over time.
Is it time to see a dermatologist?
While many young people struggle with some form of acne, most of the time the problem is controllable and does not become severe. But when routine acne progresses to the cystic stage, that is when there is cause for concern.
How to determine when a dermatologist is needed in this case? It depends on the severity of each individual. To delve further into the anatomy of cystic acne, it is important to get a mental understanding of what is actually taking place. As the pore lumen narrows, an enveloped whitehead forms on the skin’s surface which spreads to form a cystic nodule called a comedo. As the nodule takes shape, it begins to spread and drain further due to the inflammation.
At this stage of acne, it is highly recommended you seek the expertise of a licensed dermatologist as they can plan the best course of action to take and how. Due to the severity of cystic acne, treatments may vary depending on whether or not it has formed a sinus tract which is a pooling of the bacteria and the bodies natural response in containing sepsis.
In that case, routine surgery may be necessary to drain the edema, though many treatments can prevent cystic acne from reaching such a severe state. Of the brief ointments we previously mentioned, there are numerous other antibiotics both oral and topical which can be used in such an instance to include benzoyl peroxide as the main component in a milder case.
Another possibility for cystic acne treatment could include steroidal injection to freeze the lesions from growing larger and storing more bacteria.