Tubal ligation
 There are dozens of different methods of birth control available today, giving women the freedom to choose the one that is right for them, depending on individual needs, lifestyle, and reproductive goals. One of the most effective of these is tubal ligation (also known as tubectomy or “getting your tubes tied”). This is a permanent contraception and female sterilization method.
There are dozens of different methods of birth control available today, giving women the freedom to choose the one that is right for them, depending on individual needs, lifestyle, and reproductive goals. One of the most effective of these is tubal ligation (also known as tubectomy or “getting your tubes tied”). This is a permanent contraception and female sterilization method.
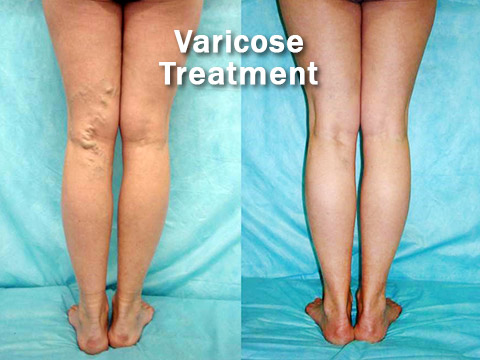
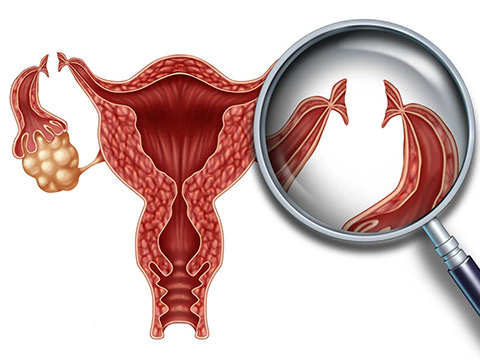
In order for conception to occur, the fallopian tubes must connect the ovaries to the uterus. In a tubal ligation, the fallopian tubes are cut (ligated) so that semen cannot travel up the tubes to fertilize the egg and eggs cannot travel to the uterus. A tubal ligation virtually eliminates the chance of getting pregnant – in the first year after the procedure, the chance of getting pregnant is less than 1 percent.
Procedure
There are several ways to perform a tubal ligation. Laparoscopy is a popular technique in which a small telescope (laparoscope) is inserted into patient’s abdomen through a small incision and the fallopian tubes are ligated with a cauterizing (heat) device, clamped with special clips, or blocked with tubal implants.
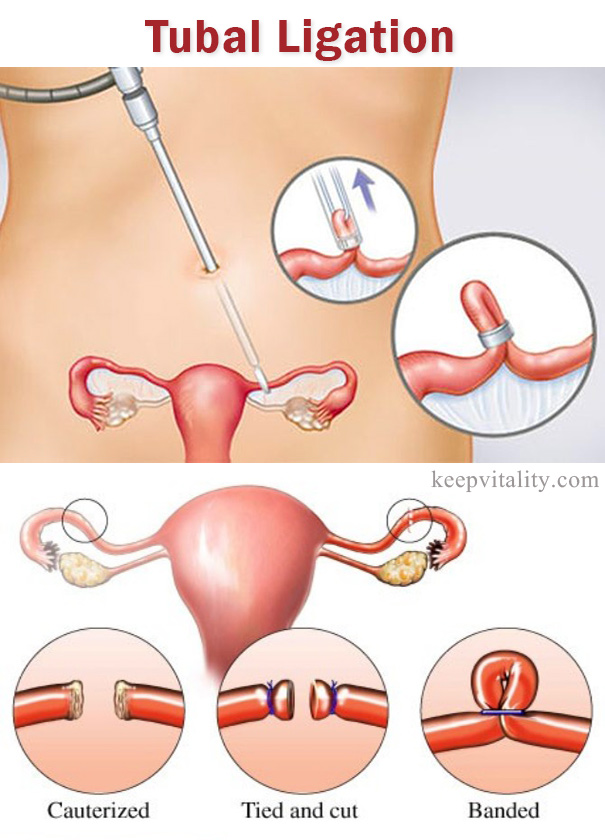
Many women choose to have a tubal ligation immediately after they give birth. If you had a caesarean section and your abdomen is still open, your doctor can perform the tubal ligation in just a few extra minutes while you are still anesthetized (called an open tubal ligation, or laparotomy). After a vaginal delivery, your doctor may opt for a method known as minilaparotomy in which a small incision is made below the navel through which your doctor raises a portion of each fallopian tube.
In most cases when this surgery is performed on an outpatient basis the procedure is considered same-day surgery (you go home the same day you have the surgery). Laparoscopy and mini-laparotomy are usually done with a regional or general anesthetic while laparotomy is usually done under general anesthesia. If you received general anesthesia, you will probably have to stay overnight.
If you choose to have a tubal ligation done immediately after you deliver, be sure to discuss this with your doctor during your prenatal appointments and arrange for it in advance. Inform your doctor of any circumstances under which you would not want him to proceed with the tubal ligation after the delivery.
Within eight hours after a tubal ligation, most women can resume relatively normal activity. After surgery, you may feel some discomfort that may last about a week, during which time you should abstain from sex and strenuous exercise. You may also experience fatigue, dizziness, nausea and bloating. If you have a laparoscopic procedure, you may feel discomfort in your shoulder or the side of your neck. This is normal and due to irritation of your diaphragm by the gas used to inflate your abdomen.
Side effects
As with any operation, tubal ligation carries some risk.
- Minor complications include infection and wound separation and affect between 6 and 11 percent of women, depending on the form of tubal ligation performed.
- Major complications include general anesthesia problems and need for a larger laparotomy incision during surgery, heavy blood loss, organ injury during surgery. Approximately 1 to 1.5 percent of women experience major complications.
A tubal ligation will not change your regular menstrual cycle, nor will it affect your libido. You will still ovulate each month (release an egg) and have menstrual periods; and you will experience menopause at the same time you would have if you had not had the surgery. Your libido may in fact increase and you may feel more relaxed with your partner because any concerns about getting pregnant have been removed.
The cost for a tubal ligation runs about $3,000 to $6,000, depending on where you live. If your doctor performs the procedure right after delivery, the costs may be slightly lower; however, if you require hospitalization, the cost will be greater. Some private health insurance companies will cover a portion of the expense.
Tubal ligation reversal
About 1.5 percent of women who have undergone tubal ligation decide to reverse the procedure, called microscopic tubal ligation reversal. However, a reversal is difficult to perform, considered major surgery, and requires a stay in the hospital. Depending on the method of sterilization used, success can range from 50 to 65 percent; however, if the previous surgery damaged much of the fallopian tubes, a reversal may not be possible at all. Up to 60 percent of women who reverse a tubal ligation subsequently conceive a viable baby, but their chances for an ectopic pregnancy increase. In addition, a reversal is an expensive procedure not covered by many insurance companies.
In-vitro fertilization (IVF) offers an alternative to surgical reversal of a tubal ligation. However, most doctors feel that if a tubal ligation can be reversed, it is preferable over an IVF procedure. A reversal requires one procedure to restore fertility, enabling the woman to have as many children as she wants, but a woman may have to undergo several IVF procedures to conceive one child.
With IVF, the woman’s eggs are removed directly from her ovaries, fertilized in a laboratory, and the viable embryos are then placed into her uterus. The tubes are simply bypassed in the process. IVF procedures are costly and not covered by most insurance companies; therefore, couples who choose this option will find that there are substantial costs incurred to obtain a pregnancy each time, as well as the possibility of unintended multiple fetuses.
The decision to make contraception permanent is never an easy one. Before you choose any sterilization procedure, ask yourself the following questions:
- How would you feel if you lost your partner to death or through a divorce and later decided you would like to have a child with another partner?
- One child could never replace another, but if you lost a child would you want to have another baby?