Plantago major
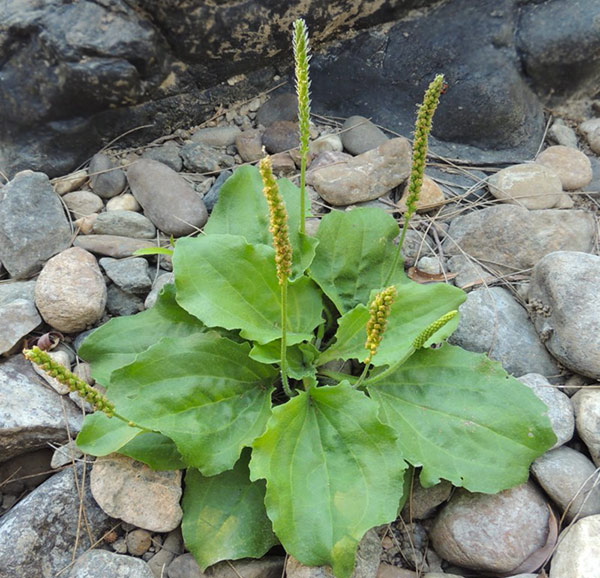 Plantágo májor (greater plantain or broadleaf plantain) is a member of the Plantaginaceae family. Plantago major contains mucilage, aucubin glucoside, minerals, vitamins C, K and factor “T” which helps to stop bleeding.
Plantágo májor (greater plantain or broadleaf plantain) is a member of the Plantaginaceae family. Plantago major contains mucilage, aucubin glucoside, minerals, vitamins C, K and factor “T” which helps to stop bleeding.
Traditional and contemporary Use: as an astringent (slightly), diuretic, antiseptic, vulnerary, cooling (leaves).
It is indicated (leaves and especially the root or seeds) for inflammation of the stomach and intestines, ulcers, and to reduce stomach pain, gastritis, enteritis, enterocolitis, loose bowels, internal wounds, hemorrhoids, abscesses, internal bleeding, dysentery, dyspepsia, chronic colitis, and to correct over acid conditions of the stomach and regulate secretions. It is especially indicated for diarrhea and bowel complaints of children.

Its reflex action, coupled with its diuretic property, aids kidney and bladder trouble. Additionally, it is quieting to coughs, and has been reported to be of some benefit in cases of tuberculosis of the lungs. Its vulnerary and coagulation factor has found application in excess menstrual bleeding, bleeding ulcers, wound dressings, abscesses, inflamed and chronic skin conditions. Historically, it has been used (in addition to the above) to treat neuralgia, dropsy, epilepsy, yellow jaundice, pain in the lumbar region, mucus in the ears, scrofula, leukorrhea, poisonous insect and snake bites, erysipelas, eczema, plus burns and scalds.
As per German commission E monograph*: Plantain herb, Plantago lanceolata “Approved herb”.
- Internal use: catarrhs of the respiratory tract, inflammatory alterations of the oral and pharyngeal mucosa.
- External use: inflammatory reactions of the skin.
- Contraindications: none known.
- Side effects: none known.
- Actions: astringent, antibacterial.
*German Commission E Monographs: published by Integrative Medicine Communications