Valerian
 Latin name: Valeriána officinális. It belongs to the genus Valeriana, family Valerianaceae. Also known as: all-heal, amantilla, capon’s tail, setwal, garden valerian, garden heliotrope. Valerian has been used successfully to guard against sleeping disorders, restlessness, anxiety, depression, insomnia, headache, menstrual cramps, intestinal cramps and is useful as a muscle relaxant. Parts used: rhizome, root.
Latin name: Valeriána officinális. It belongs to the genus Valeriana, family Valerianaceae. Also known as: all-heal, amantilla, capon’s tail, setwal, garden valerian, garden heliotrope. Valerian has been used successfully to guard against sleeping disorders, restlessness, anxiety, depression, insomnia, headache, menstrual cramps, intestinal cramps and is useful as a muscle relaxant. Parts used: rhizome, root.
Introduction
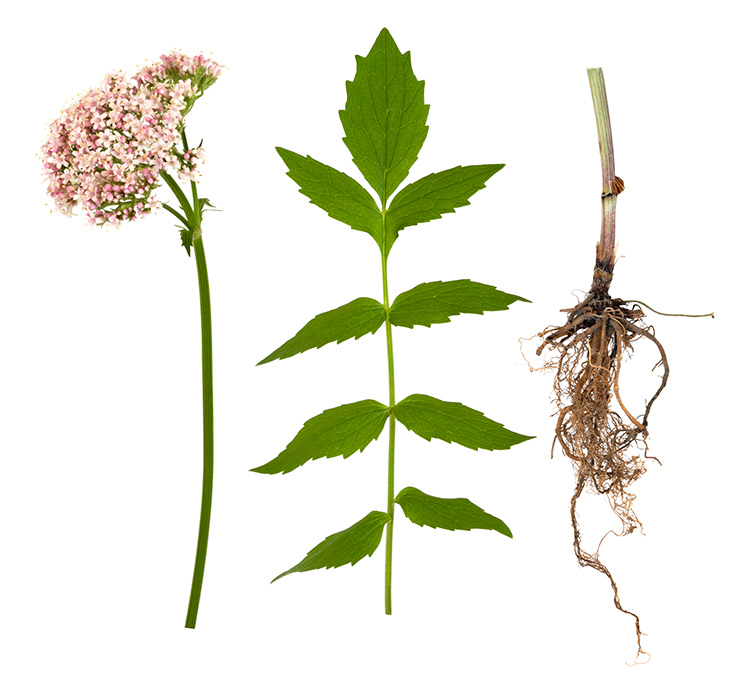
Valerian is an erect perennial growing to a height of 4 to 6 feet with pinnate, divided leaves and pink flowers. Valerian and its extracts are contained in singly and in combination in literally scores of drugs and teas that are currently available on the European and US market. Consisting of the dried rhizome and roots (underground parts) of Valeriana officinalis, the drug continues to be used after more than 1000 years as a valued tranquilizer and calmative in cases of nervousness and hysteria. Other species of Valeriana also contain active principles and are similarly utilized.

Chemical & nutrient content
Key constituents in valerian are volatile oil (up to 1,4%), including bornyl acetate, beta-caryphyllene, iridoid compounds (valtrate, isovaltrate) that appear to have anti-tumor, anti-spasmodic, anti-convulsant and sedative properties, with the highest concentration occurring in the roots.
Other constituents:
- alkaloids – valerine, chatinine, valerianine;
- valeric acid, formic acid, acetic acid;
- gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA);
- camphene, glycosides, tannins, pinene;
- calcium;
- magnesium;
- resin and gum.
Historical use
Valerian has been used since Roman times as a relaxant, sedative and sleep aid. It was known to Dioscorides in the 1st century AD, who named it “phu”, the sound of the word reflecting its unpleasant smell.
Actions and properties
- Antispasmodic
- Anodyne
- Carminative
- Nervine
- Brain stimulant
- Expectorant
- Diuretic
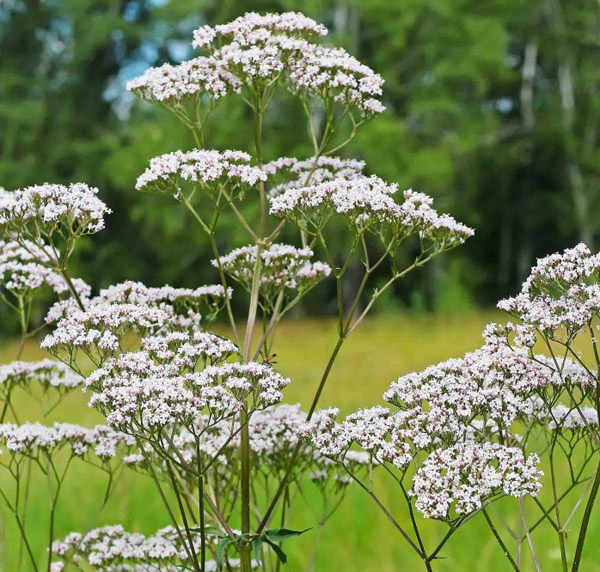

Medicinal use
Today, valerian is widely used as a sedative to induce sleep and calmness in small quantities. It works by relaxing the central nervous system and smooth muscle tissue. Studies have shown this herb also reduces high blood pressure, has anti-tumor effects and suggest that it has anticonvulsant effects. Valerian can relieve gas and intestinal cramps, and may be useful in treating low fevers and colds.
 Valerian is able to reduce sensitivity to some of the ‘noise’ of the central nervous system, without interfering with activity or co-ordination, and finds its primary application to states of tension, irritability or spasm. Its antispasmodic action lending further to states of visceral tension, such as nervous bowel, dyspepsia, cramp, migraine and other vasospasms and similar disorders.
Valerian is able to reduce sensitivity to some of the ‘noise’ of the central nervous system, without interfering with activity or co-ordination, and finds its primary application to states of tension, irritability or spasm. Its antispasmodic action lending further to states of visceral tension, such as nervous bowel, dyspepsia, cramp, migraine and other vasospasms and similar disorders.
It has been recommended for epilepsy but that has not been supported by research, although, one of its ingredients, valproic acid, is used as an anticonvulsant and mood stabilizing drug. Valine, an essential amino acid, is named after this plant.
There is a misconception that Valium is derived from valerian, it is not. Valerian herbal supplements are the much safer and milder sedative. Valium can be an addictive drug. However, valerian is not addictive and produces no withdrawal symptoms. The sedative effect of valerian is not exaggerated by alcohol or barbiturates.

Typical dosage
Valerian products are most commonly available in commercial form as infusions, tinctures and capsules. Recommended usage:
- Infusion: One cup before bedtime.
- Tincture: 1 tsp. per 1/2 cup water or 10 – 30 drops taken up to three times daily.
- Capsules: Take one capsule up to three times daily.

Side effects /Cautions
Valerian is generally a safe herb, but since it may create a sleepy effect it is best not to drive while taking valerian. It is especially important to follow the recommended dosages on the labels of valerian products. An overdose of valerian could result in a dangerous weakening of the heartbeat. If you should experience an upset stomach while taking valerian, try taking your recommended dosage at mealtime.
It is listed in the Federal Drug and Administration’s list of herbs regarded as safe. As with all herbal nutrition supplements, valerian supplements should only be used in amounts typically recommended for medicinal purposes and you should always consult with a health professional first, especially if you are pregnant, nursing or taking prescription medications.
Contraindications: With other sedative drugs and/or anti-depressants and/or alcohol